With 20% faster performance than .Net Core 1.X, core 2.0 is in the lime light. Optimizing to the core the .Net core 2.0 is the next big thing for the Microsoft Developers.
A modular framework uniting the MVC and Web API into a single programming Model running on .Net framework or .Net core run-time but can run on any platform. Highly flexible in deploying to cloud and since cross platform, the demand among the developers increases.
Asp.Net Vs Asp.Net Core
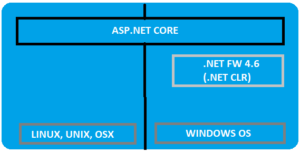
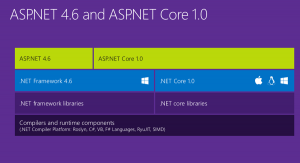
Asp.Net Core is runtime and executes applications built for it. Asp.Net core application is also .Net Framework application because of the .Net core libraries are used for both the core and .Net framework applications. Here the thing to notice is Asp.Net core is built on top of both .Net framework & .Net Core where as the Asp.Net is now being termed as .Net Framework. Check the image below (from Blogs )
Asp.net Core libraries/dependencies are self-contained, most of the packages are downloaded from Nuget but can run on windows, linux & Mac where as in Asp.Net the packages are self contained but can only run on windows.
Based on the .Net Core CLI (Command Line Interface) on which the IDE (Integrated Development Environment) relies on. It is the cross platform tool chain for developing .Net applications irrespective of the platform.
Visual Studio as IDE has support for running on Windows and MacOS. Visual studio code can be used as IDE on windows, MAC and Linux systems as well.
Directly .Net Core CLI can be used on the Command window to execute the .Net applications.
dotnet new console dotnet build --output /build_output dotnet /build_output/my_app.dll
More about .Net Core 2.0
The latest of the Core versions now in the market. With the command line interface it is just few command away from creating a .Net Core 2.0 application. .Net core 2.0 now comes with the Entity framework 2.0. To start with the .Net Core 2.0, one just needs to download and install the .Net core 2.0 SDK
Creating a small and simple application using CLI

.Net Core 2.0 has a lot of performance improvements. One of the best improvements in .Net Core 2.0 is Razor Pages. Razor pages in .Net core 2.0 MVC projects are enabled by default using the services.AddMvc();
Now whats new in the integration of Razor Pages! In the Razor Pages now there is no direct coupling with the hard bound Controller we used to create and adding views to them and then routing through the controllers and Actions.
Now, we can directly create a folder and add a .cshtml page. For example,
We add a cshtml file named- “CoreTest.cshtml”
@page <h1>Hello Core 2.0!</h1>
Here the routing would be “/CoreTest”. Simple and Crisp! Interesting thing is the precious page route was /CoreTest, now it can be customized and rerouted to the customized route to suppose “/core-test”.
services.AddMvc()
.AddRazorPagesOptions((opts) =>
{
opts.Conventions.AddPageRoute("/CoreTest", "core-test");
});Razor compilation is easier and is automatically compiled during the publishing of the package or the application.
MvcRazorCompileOnPublish is the property that is set to true by default. We can set it to false to avoid this auto compilation.
<PropertyGroup> <TargetFramework>netcoreapp2.0</TargetFramework> <MvcRazorCompileOnPublish>false</MvcRazorCompileOnPublish> </PropertyGroup>
The .Net core 2.0 simplified the Program.cs class file as compared to the .Net Core 1.x.
For .Net Core 1.X
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
var host = new WebHostBuilder()
.UseKestrel()
.UseContentRoot(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory())
.UseIISIntegration()
.UseStartup()
.UseApplicationInsights()
.Build();
host.Run();
}
}For .Net Core 2.0
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
BuildWebHost(args).Run();
}
public static IWebHost BuildWebHost(string[] args) =>
WebHost.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.UseStartup()
.Build();
}Now migrating a .Net Core 1.X project/application to .Net Core 2.0 is easy as well. We will cover the Migration Steps in the upcoming articles without letting down the scope of this article.
Lets create a MVC Web Application from Command Line
Using the command line interface we can create different types of dotnet applications without using the GUI. The commands to be used are:
- dotnet new -type:- There are different types of dotnet application that can be created using the command new and specifying the type. Like earlier we created a console application, so the command was “dotnet new console”. Similarly for a normal web project, the command would be “dotnet new web”. For MVC application, the command is “dotnet new mvc”.
- dotnet restore:- Restores the packages and assemblies while compiling the project. This is auto run during the new project creation process as well.
- dotnet build:- This is the build command which runs before running the application required to compile the application.
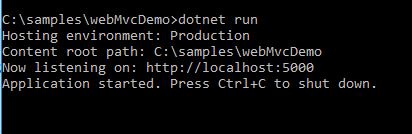
- dotnet run:- This command actually runs the appliction, hosting using the IIS and localhost port.
The entire commands on CMD looks like below:
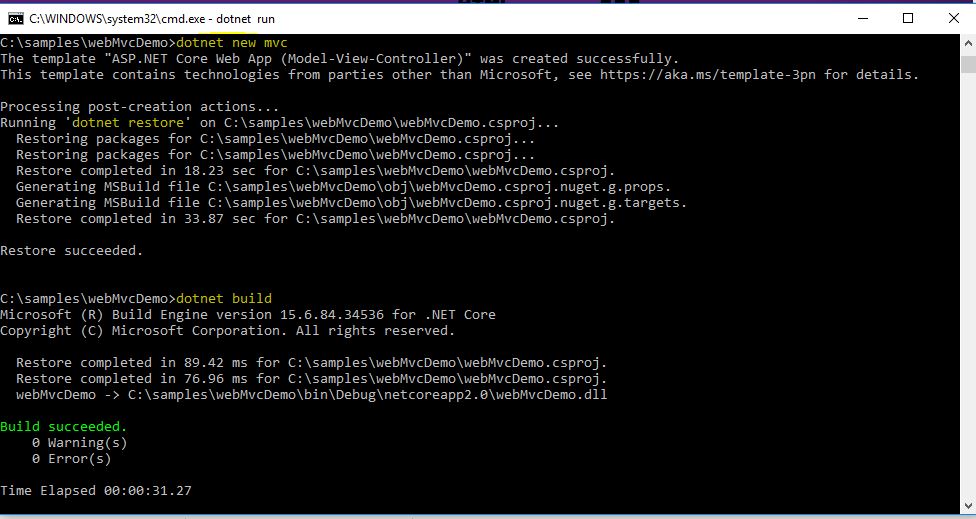
The project after creation looks like:

The run command on CMD looks like:
There are many more interesting features introduced in .Net Core 2.0. We will be covering the features in detail in the upcoming articles.
]]>Asp.Net Core is completely re-written prior to earlier versions works on .Net framework. Asp.Net was developed with main focus to make it cross-platform! Yes Asp.Net core is now cross platform. It has gained popularity in quick time for modern day web development. One go cloud development with configurations made easy, with self hosting process with IIS and many more features added to Asp.Net core which makes it stand tall!
Cross Platform!
Yes! you read it right, Asp.Net core is now cross platform. The Asp.Net core CLR now has now WPF & winforms. It is built to code once and run on any platform. We can now have the .Net framework installed on Linux, Unix or OSX.
.Net Core CLR has joined the open source community and is on github. Anyone can contribute now on github for the .Net Core. Asp.Net Core applications can run both on .Net earlier frameworks and also on .Net core, which puts a great benefit for the developers. .Net Framework 4.6 is the same .Net we have been using and continue to develop the same way. .Net Core gives a platform to generate cross-platform solutions. But .Net 4.6 is stable and .Net core is under progress.
Merged stack MVC & Web API
Now this seems interesting. What? MVC & Web API merged!! Yes it is, in Asp.Net core we will have the merged stack of MVC and API and moreover Webforms is completely gone! Earlier we were required to add more than one Web project, one for MVC and one for Web API. But in Asp.Net core, we need to have only one project.
Multiple inbuilt tools are being used with .Net Core to build web applications with ease like NPM used for tools support, Client side support using Bower, Grunt & Gulp for building automatically, & as usual Nuget for .Net packages.
.Net Core application with Command Prompt & VS Code
Once we have installed .Net core framework in our system, since it is open source the .Net Framework can be accessed and projects can be maintained through command prompt.
Open command prompt, and hit “dotnet”. It will result the entire information of the .Net framework.
To create a new project using the dotnet templates, using scaffolding in VS IDE. The same scaffolding is also possible in the command prompt. With the command, “dotnet new”. This creates the scaffolding and restores the packages required if not exist.
Then the scaffolding templates:
Here we see multiple templates
Choose one of the templates setting the path where the project needs to be added. Lets create a console application as of now in one of our drives. To add a new console application, the command goes like below:
Here a new project is created, a console application for “Hello World”. Then when you run, you get namespaces missing error and navigating into the directory, you find the bin and obj folders go missing. Thus the error shown below:
Thus, restoring the packages solves the issue.
“dotnet restore”
This resolves and restores the required default packages for the console application.
Then build the project in order to ensure the code is errorless.
“dotnet build”
After build succeeds, then run the project to get the out put.
“dotnet run”
Output goes as below:
The same can be achieved in the terminals of Linux OS & Mac OS, just .net Core framework needs to be installed on the OS, which is why .Net core is developed to make it cross platform.
Upcoming articles we will look into the more details of the dotnet core. Creating Web applications using .net core and the MVC6.
An interesting topic to share again! Recently while I was using GIT, the options in the browser on the GITHUB site, launched the application installed on my system! I wondered if that is possible I can run any exe from my web application and create wonders!
Nice story huh! Actually, that is possible and I will be sharing the process how we can achieve the same from code.
I will be using windows registry to register my exe to be pinged from any web application. Now wondering what is Windows Registry!
The Windows Registry is a hierarchical database that stores low-level settings for the Microsoft Windows operating system and for applications that opt to use the Registry..Wiki
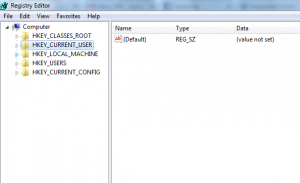
Now yes, windows registry is an important section of the windows operating system having all the low level settings, but very essential for the applications to run on the OS. Windows registry is basically used to store all the important information for the software programs, hardware devices connected. There are basically few root keys pre-defined under the registry belt!
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE:- Setting are stored which are local or specific to the system.
- HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG:- All the gathered run time information are contained withing this key. This key is never in the memory, but generated at the boot time process.
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER:- Settings that are valid/applicable to the current logged in user on the system.
- HKEY_USERS:- All sub keys corresponding to the current user are stored.
- HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT:- Information about any registered application on the system is contained.
Each of the above root keys have sub-keys attached to them.
For example: HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Classes\ means ‘Classes’ is the sub key of the ‘Software’ sub key under the ‘HKEY_CURRENT_USER’ root key.
We will be creating a key inside the HKEY_CURRENT_USER in order to ping the exe. We have chosen this root key as that would not require any Admin access to add/edit any key inside this root. So the exe can be pinged by any user.
Diving into the code!
Here, what we would be doing is, we will be creating one console application(.exe), which will act as a medium to add a registry sub key to the “HKEY_CURRENT_USER/Software/Classes”. The same console application will be used to be executed/run from the web application. alert is the key command name which is used for this purpose.
using Microsoft.Win32;
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
namespace WMConsole
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Listening..");
//Gets the current location where the file is downloaded
var loc = System.Reflection.Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().Location;
if (!Directory.Exists(@"D:\Console\"))
{
System.IO.Directory.CreateDirectory(@"D:\Console\");
}
//Creates the Downloaded file in the specified folder
if (!File.Exists(@"D:\Console\" + loc.Split('\\').Last()))
{
File.Move(loc, @"D:\Console\" + loc.Split('\\').Last());
}
var KeyTest = Registry.CurrentUser.OpenSubKey("Software", true).OpenSubKey("Classes", true);
RegistryKey key = KeyTest.CreateSubKey("alert");
key.SetValue("URL Protocol", "wnPing");
key.CreateSubKey(@"shell\open\command").SetValue("", @"D:\Console\WMConsole.exe %1");
}
}
}
Understanding the code!
In the above snippet, we are first creating folder where the same exe will be downloaded from the web application and stored. The path is being dynamically generated and used.
- Then we open the existing root key of the registry, i.e. HKEY_CURRENT_USER through the Registry class field “CurrentUser” and the “OpenSubKey(“Software”, true)”, opens the instance of the sub-key or allows the write access to it. Same with the sub-key “Classes” which lies under the Software key.
- Then, we are creating a new key using the “CreateSubKey(“alert”)” command, with the name “alert”.
- Then we set the value to the sub key “alert”, as “URL protocol” and the name to be used in the anchor tag in web application as “wnPing”.
Subkey alert created, also gets a subkey added to it in the following hierarchy:
shell->open->command
and to this, the value is set as the path to the exe file, which will run.
Once the registry is created, we add the below anchor tag for the exe application to be triggered from any web.
<a href="alert:wmPing">Click to trigger</a>
And done, click to see the magic!
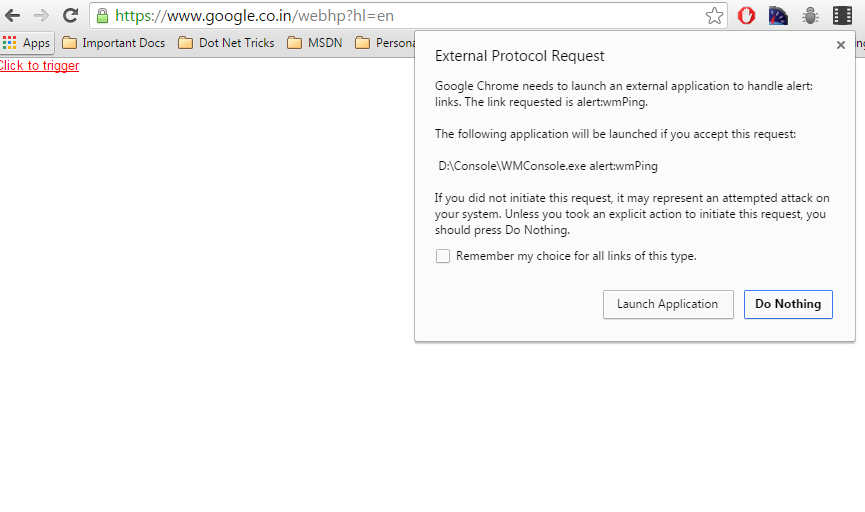
The above window comes up, asking user to Launch the application. Done!!
You can always click the check box to remember the action, if you want the exe to run in the background without prompting.
Conclusion
This is it. I hope you find this topic interesting and try the same. This can be helpful in any web application when you are dealing with any hardware components attached to local client systems and your server needs input from them.
Please share your thoughts and views on any improvement!
Keep learning and keep sharing!
Introduction
Here I would be demonstrating an application to chat and chat private as well, using SignalR.
Before that we need to know first what is SignalR! SignalR is an open and free library which can be used to have real-time functionality integrated to your web applications. There are a hell lot of areas where SignalR can come handy to make your application more handy and more integrated and more responsive to the end user as well. Real-time means having your server respond as quick as possible to the client as and when a request is made.
Now, take for an instance, we have a requirement to show the user uploading a file, the percentage of that file been uploaded on the server. Or I had come across a scenario where, we had to show the end user, who would be uploading a CSV file with ‘n’ number of rows and process each row for some validations. End user would be wondering what would be going on in the back-end. So, would it be great if we could show him how many rows have been processed and how many are left out! Similar to a progress window. Here, comes the SignalR magic!
Most of us think SignalR would be useful in making chat applications, but NO!,it has much more than just chat! I don’t think the makers of SignalR would have a thought in mind to make a chat application out of it! 
Much of a story now! Lets get into a bit of theory!
Theory
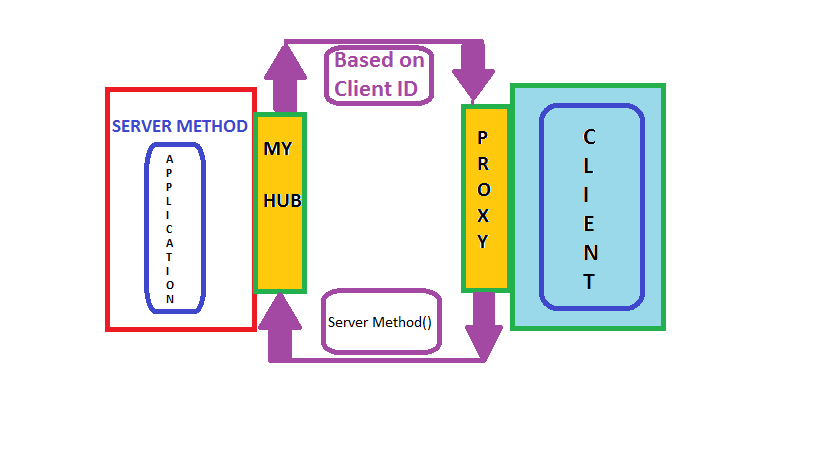
We will look into a simple image below and from that image we will try and gain some knowledge on the flow:
Now a days, every application requires a load of server response in the real time to sustain in the market, as the user expectations have raised high.
Remote Procedure Calls (RPC) is the concept that takes place in the SignalR internally. SignalR provides an API which helps in making the RPC between the server and the client. Actually, from the client side, server side functions are called using JavaScript, once the connection to server is set. The SignalR API also helps creating connections and manage them when required. In simple terms, SignalR provides connection between server and client, letting server to call the funcitons on the client side and from the client side, calling the server side. That somehow is called “Server-Push”.
SignalR starts with HTTP and then to a WebSocket if connection is available. From Wiki,
“WebSocket is a protocol providing full-duplex communication channels over a single TCP connection.”
An advantage of using WebSocket is it can be used by both client and server applications. WebSocket is considered to be the most efficient and consistent medium of communication as, it has the ability to manage server memory in a proper manner and being a full duplex communication, has low latency. These are the considerations made with SignalR which make it more efficient.
The SignalR decides the transport based on the browser, i.e. if the browsers support the kind of transport required by the SignalR. We will discuss the kinds of transports next:
HTML 5 Transports
- WebSockets as we have already discussed. This transport is considered to be true-persistent, creating a two way connection between client and server if the browsers support.
- Server Sent events also called Event Source, which is supported by all browsers except IE.
Comet Transports
Comet usually,is a web application model in which a long-held HTTP request allows server to post data to a client (browser).
- Forever frame This is supported by Internet Explorer only. Creates a hidden frame making a request to endpoint on the server. Server keeps pinging client or sends script to the client, thus providing a one way connection, creating a new connection on every request.
- Ajax Polling This is actually long polling, which is never persistent. This polls the request and waits until and unless the response is received from the server. This introduces latency and the connection resets.
Practical
We will be creating a chat application in order to explain the flow of SignalR. We install the SignalR, create a hub to which the client will interact, calling the server methods and in return the server responds and interact with the client.
You can directly add a new project in VS for the SignalR or create an MVC project and install the SignalR package/libraries from the Nuget.
PM > Install-Package Microsoft.AspNet.SignalR
This is download all the dependencies required for the SignalR.
After the successful installation, the above dll’s or packages are installed into your project.
There will be a class file which needs to be added to the root of your project, which would look like:
using Owin;
using Microsoft.Owin;
[assembly: OwinStartup(typeof(SignalRChat.Startup))]
namespace SignalRChat
{
public class Startup
{
public void Configuration(IAppBuilder app)
{
// Any connection or hub wire up and configuration should go here
app.MapSignalR();
}
}
}This is OWIN based applicaiton. Every OWIN application will have a startup.cs class, where the component for the application pipeline are added. The OWIN attribute which specifies the type of property, specifying the project’s start up and the configuration method, sets up the SignalR mapping for the App.
There will be another two script files that would be added as we install the packages for SignalR.
These script files are mandatory to be loaded onto the .cshtml page in order to activate the SignalR.
Lets look into the code straight away:
We need to add a new hub class inside a Hub folder. Lets name that LetsChatHub.cs, which would look like:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using Microsoft.AspNet.SignalR;
namespace LetsChatApplication.Hubs
{
public class LetsChatHub : Hub
{
public void Send(string name, string message,string connId)
{
Clients.Client(connId).appendNewMessage(name, message);
}
}
}The above send method accepts the parameters, name (which you would be giving once you navigate onto the url), the message (which the user would be sending from the UI). The other parameter is connId, which would help us have chat private and not send to every user who navigates to the site. If you would like to have every user receive and send the messages who navigates to the URL. To allow every users the access, the code you change as below:
namespace LetsChatApplication.Hubs
{
public class LetsChatHub : Hub
{
public void Send(string name, string message)
{
Clients.All.appendNewMessage(name, message);
}
}
}The Send method, is requested from the client with the parameters after the connection is set on the client side and once the server receives the request, it processes and sends back the response to the client, using the appendNewMessage. This appendNewMessage method is added on the client side to receive the response and display on the UI to the client.
You need to add a controller, lets suppose: “LetsChat” with an action “LetsChat”, add a view to that with the below code to it.
The client side code would look like below:
@{
ViewBag.Title = "LetsChat";
}
<h2>Lets Chat</h2>
<link href="~/Content/sweetalert.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<div class="form-group col-xl-12">
<label class="control-label">Your connection Id</label><br />
<input type="text" class="col-lg-12 text-primary" id="frndConnId" placeholder="Paste your friend's connection Id" /><br /><br />
<label class="control-label">Your Message</label><br />
<textarea type="text" class="col-lg-10 text-primary" id="message"></textarea>
<input type="button" class="btn btn-primary" id="sendmessage" value="Send" /><br /><br />
<img src="~/Content/smile.jpg" width="20" height="20" id="smile" style="cursor:pointer"/>
<img src="~/Content/uff.jpg" width="20" height="20" id="ufff" style="cursor:pointer" />
<div class="container chatArea">
<input type="hidden" id="displayname" />
<ul id="discussion"></ul>
</div>
</div>
<br />
<input type="hidden" id="connId" />
<!--Reference the autogenerated SignalR hub script. -->
@section scripts {
<script src="~/Scripts/jquery-1.10.2.min.js"></script>
<script src="~/Content/sweetalert.min.js"></script>
<script src="~/Scripts/jquery.signalR-2.2.0.min.js"></script>
<script src="~/signalr/hubs"></script>
<script>
//var userName = "";
//var sessionVal = '';
$(function () {
// Reference the auto-generated proxy for the hub.
var chat = $.connection.letsChatHub;
debugger;
// Create a function that the hub can call back to display messages.
chat.client.addNewMessageToPage = function (name, message) {
// Add the message to the page.
$('#discussion').append('<li><strong>' + htmlEncode(name)
+ '</strong>: ' + htmlEncode(message) + '</li>');
};
// Get the user name and store it to prepend to messages.
swal({
title: "Lets Chat!",
text: "<span style='color:#f8bb86;font-weight:700;'>Enter your name:</span>",
type: "input",
html: true,
showCancelButton: true,
closeOnConfirm: true,
animation: "slide-from-top",
inputPlaceholder: "Your Name"
},
function (inputValue) {
userName = inputValue;
if (inputValue === false) return false;
if (inputValue === "") {
swal.showInputError("You need to type your name!");
return false;
}
$('#displayname').val(inputValue);
});
// Set initial focus to message input box.
$('#message').focus();
$('#message').keypress(function (e) {
if (e.which == 13) {//Enter key pressed
$('#sendmessage').trigger('click');//Trigger search button click event
}
});
$("#smile").click(function () {
});
// Start the connection.
$.connection.hub.start().done(function () {
$('#sendmessage').click(function () {
// Call the Send method on the hub.
var connId = $("#connId").val();
var frndConnId = $("#frndConnId").val();
var finalConnId = frndConnId == "" ? $.connection.hub.id : frndConnId;
chat.server.send($('#displayname').val(), $('#message').val(), finalConnId);
$("#connId").val($.connection.hub.id);
if (frndConnId == "") {
swal("You connection Id", $.connection.hub.id, "success");
}
// Clear text box and reset focus for next comment.
$('#discussion').append('<li><strong>' + htmlEncode($('#displayname').val())
+ '</strong>: ' + htmlEncode($('#message').val()) + '</li>');
$('#message').val('').focus();
});
});
});
// This optional function html-encodes messages for display in the page.
function htmlEncode(value) {
var encodedValue = $('<div />').text(value).html();
return encodedValue;
}
</script>
}
Lets Chat
We have a normal UI in place to add your message and send button to call the server methods.
Lets understand the code above part by part.
var chat = $.connection.letsChatHub;
Here, we set the connection to the Hub class. As you can notice here, letsChatHub, is the same hub class file name which we added to set up the server. The convention as follows, the intial of the methods or the class name starts with lowercase. From here, we use chat to access the Send method.
$.connection.hub.start().done(function () {
$('#sendmessage').click(function () {
// Calls the Send method on the hub.
chat.server.send($('#displayname').val(), $('#message').val(), finalConnId);chat.server.send,is self explanatory, it sets the chat connection to call the server Send method once the connection is set and started.
chat.client.appendNewMessage = function (name, message) {
//
}This is called, when the Server receives the request and calls back the method on client side.
How the sample would work!
The sample provided for download, will be having few instructions to follow:
- When you navigate to the LetsChat/LetsChat route, an alert would pop up asking you for the name with which you would like to chat. Sweet Alert !!
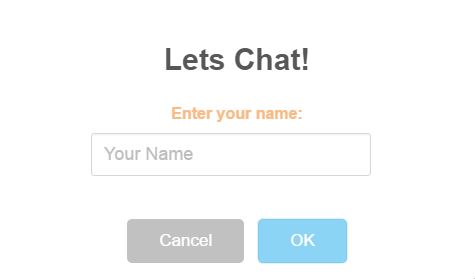
- Once you enter the name, you see a textbox which asks you for “Your friend’s connection Id”, but since you are starting the chat, you just send a message, and another pop up comes up, with your connection ID, which you need to share with your friends to share your message. Remember, only those who have your ID use it while chatting will be able to see and send through messages to you.
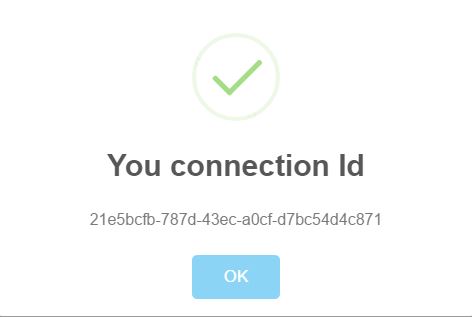
- When you friend navigates, he ought to generate his connection ID and share with you inorder to set up your connection completely. Thus, you need to have the connID to whom you will be sending and vice-versa with your friend as well. Then just chat!!

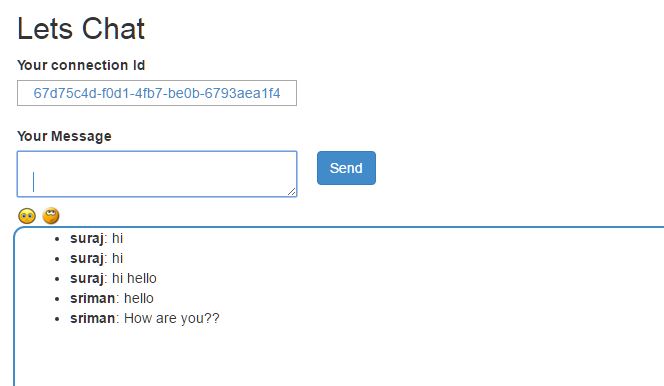
If you would want to send message to all and make that common, then use the Clients.All code snippet to send all.
Another interesting thing, which was figured out is, the use of @section scripts{}, that lets the Signal R scripts render and active on your page and also using the @section scripts provides your code a good outlook.
Share and Send files using SignalR!!
Ooops!! Nice question right!
It is ideally not advised, rather I would not recommend to send or share files using Signal R. There always is better way to accomplish that. The idea would be using API, you can have an upload area, and use SignalR to show the progress and once upload completes, update the user regarding the completion and generate a download link on the UI for the users to download and view the file.
This is not always the best idea, but is just another idea. 
Conclusion
This is just a simple Chat application, which you can use to chat with your friends, if you host on Azure or any other domain. But again,SignalR is not just this much. There is a lot of other effective use of SignalR. Will be sharing more utility of SignalR in few articles more.
References
]]>With an anticipation and hope, this article would be an interesting and effective somehow. This article will be covering the Asp.Net 5’s MVC6 Welcome application. a brief about the all new concepts of MVC6 and the new structure it beholds. Then we create our first Welcome application and then have a walk through of the new Azure Portal and deploy our first web application.
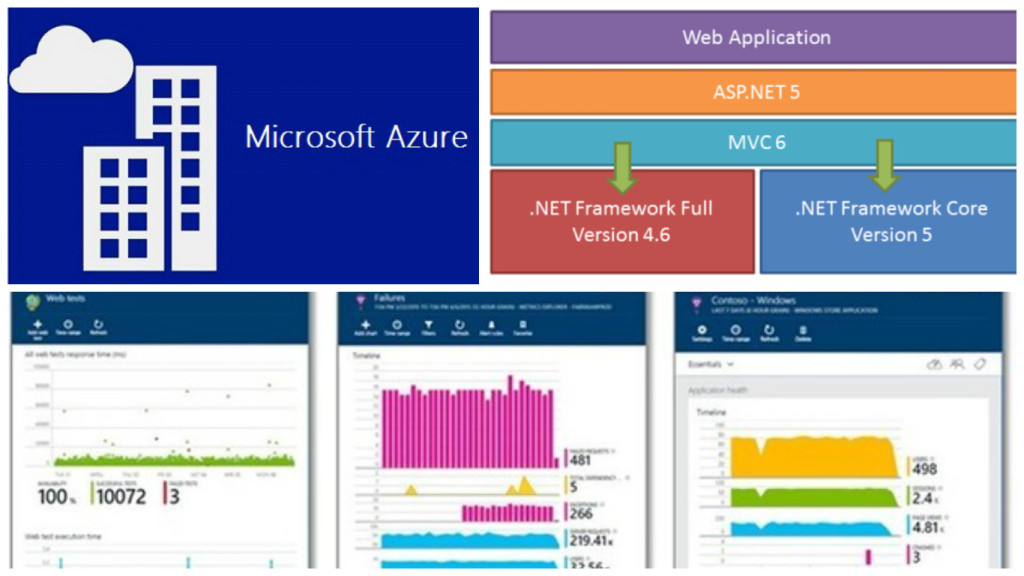
The above image is all that we will be covering in our article.
Get Started
A perfect blend of cloud and web application is what Asp.Net 5 is intended for. Asp.Net 5 is now being called off as .NET core is what that stands out today. It is a framework with open source & cross platform for building cloud based web applications. Here Azure comes integrated to the Visual Studio applications. Web applications either can be deployed to cloud or be running on On-premise. .Net core is available on Visual Studio 2015 build. You can download the community edition of the Visual Studio which is actually free. 
Community Edition Download. Give a try for sure!
.Net 5 core contains a small optimized run time environment called “CoreCLR” One more important point to note is, .Net Core is opensource and the progress can be updated on Github. They have the code exposed and the build can be tracked easily. .Net core is said to contain a set of libraries known as “CoreFx”. Below are the links to the Github. Just have a look:
Another important benefit is termed as “Portability”. What this means is, we can package and deploy the Core CLR which can in turn help you eliminate the dependency on the installed version of .Net framework. Multiple application running on different versions of CLR can be set ups well. This is the magic the team wanted to result out, which is great!
With .NET 5 and VS 2015 comes MVC6 into picture. Microsoft builds are moving faster than the world! 
When I first looked at the structure of the Solution when i added a new MVC project, I was like What!!

Where is Global.asax.cs? Where is Web.config, App_Start?. Did I download the correct files and selected the correct template. These sort of questions were flickering in my mind. When ran the application it ran successfully as well. Strange!!
Let’s have a small trip into the MVC6
Unified MVC Controllers
MVC6, the merger, the blend of three frameworks, i.e. MVC, Web API2 & Web Pages. Previous versions of MVC, while adding a new template would prompt to check whether we want Web API along with MVC. Here we select the MVC project and we get the opportunity to work with API as well.
In previous versions there were two base controller classes, separate for normal controller and also for the Api controller, i.e. ApiController
public class TestController: Controller {
}
public class ApiTestController ; ApiController {
}In earlier version as shown above, the controller base class were from System.Web.MVC.Controller and for API, System.Web.Http.ApiController. But in MVC6 it is only one, i.e. Microsoft.AspNet.Mvc.Controller.
Different style of HTML helpers
In MVC6 there comes a new title termed as Tag Helpers. They make life much more simpler. How! We will get to know once we see the code snippet.
For normal web pages, as we know the HTML helpers are defined within the System.Web.WebPages.Html under System.Web.WebPages
, whereas in MVC6, it is under the System.Web.MVC assembly..
The HTML helpers which we used to use in Razor or ASPX, were quite difficult for normal HTML developers to understand (suppose designers). Now i MVC6 that has been simplifies using the Tag Helpers.
@using (Html.BeginForm())
{
@Html.LabelFor(m => p.EmpName, "Employee Name:")
@Html.TextBoxFor(m => p.EmpName)
<input type="submit" value="Create" />
}But in MVC6 ,
@model AzureDemoProject.Models.Employee @addtaghelper "Microsoft.AspNet.Mvc.TagHelpers" <form method="post"> <div><label>Employee Name:</label> <input type="text" /></div> <input type="submit" value="Save" /> </form>
Now the second snippet looks more like HTML friendly and also a bit simple.
Mr. Damian Edwards, has posted the source code on Github which has examples of Tag Helpers. Please go through for better live understanding
Git Hub Tag Helpers Download and play around.
Support for Grunt, NPM & Bower
These are the latest trending front end development tools. These are quite new to me as well,  but will be learning and posting articles on these as well in coming days. Stay tuned!!
but will be learning and posting articles on these as well in coming days. Stay tuned!!
Ok branding apart,  lets have a brief idea on what these are.
lets have a brief idea on what these are.
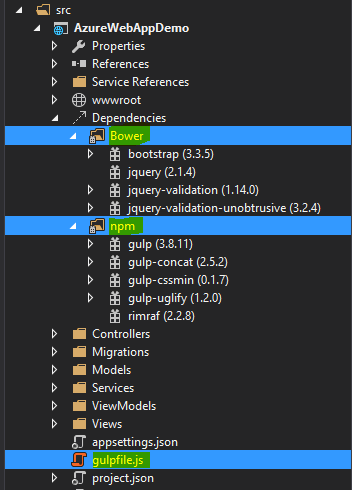
Bower:-This is a client side item added by default to MVC6 project. If not added, then Right click on the project-> Add->New Item
->Installed(Client Side)-> Bower.json. You can find then the file is already installed. The file is inside the wwwroot->lib->bootsrap->bower.json. As you open up the file, you can find the client side tool packages added to the project and their versions. Thus, we got to know that the bower is a client side package manager which is used to add the front-end packages like bootstrap, jQuery, angular, etc.
Grunt:-In MVC6 project when we add, we can find the gulpfile.js, this is kind of an alternative to the Grunt as both perform the same kind of functions. The operations they perform is minification, cleaning, concatenation, etc. of both js & css files.
NPM:- Node Package Manager is present under the project with the name project.json. This holds the dependencies and their versions required by the web application we have set up.
"dependencies": {
"EntityFramework.Commands": "7.0.0-rc1-final",
"EntityFramework.MicrosoftSqlServer": "7.0.0-rc1-final",
"Microsoft.ApplicationInsights.AspNet": "1.0.0-rc1",
"Microsoft.AspNet.Authentication.Cookies": "1.0.0-rc1-final",
"Microsoft.AspNet.Diagnostics.Entity": "7.0.0-rc1-final",
"Microsoft.AspNet.Identity.EntityFramework": "3.0.0-rc1-final",
"Microsoft.AspNet.IISPlatformHandler": "1.0.0-rc1-final",
"Microsoft.AspNet.Mvc": "6.0.0-rc1-final",
"Microsoft.AspNet.Mvc.TagHelpers": "6.0.0-rc1-final",
"Microsoft.AspNet.Server.Kestrel": "1.0.0-rc1-final",
"Microsoft.AspNet.StaticFiles": "1.0.0-rc1-final",
"Microsoft.AspNet.Tooling.Razor": "1.0.0-rc1-final",
"Microsoft.Extensions.CodeGenerators.Mvc": "1.0.0-rc1-final",
"Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration.FileProviderExtensions" : "1.0.0-rc1-final",
"Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration.Json": "1.0.0-rc1-final",
"Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration.UserSecrets": "1.0.0-rc1-final",
"Microsoft.Extensions.Logging": "1.0.0-rc1-final",
"Microsoft.Extensions.Logging.Console": "1.0.0-rc1-final",
"Microsoft.Extensions.Logging.Debug": "1.0.0-rc1-final",
"Microsoft.VisualStudio.Web.BrowserLink.Loader": "14.0.0-rc1-final"
},
"scripts": {
"prepublish": [ "npm install", "bower install", "gulp clean", "gulp min" ]
}As we can see in the above snippet, which is just a part of the project.json file. This is to show the default dependencies added to the project and the pre publish scripts mentioned. When we suppose add a new dependency, suppose I try and add System.Linq, it will list up the Nuget package as intellisense and then we add the version which also comes under the intellisense. Like below image:
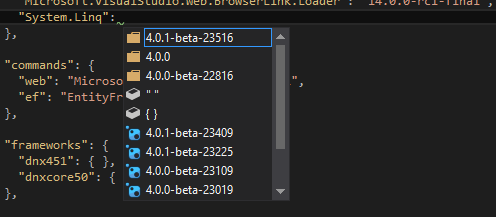
Then after hitting Ctrl+S, the restoring of the references packages starts.
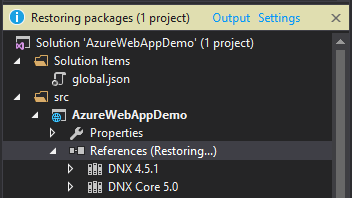
Then we see the references added. For more information on the project.json file and its contents, please visit the below link:
Project.json
Integration to Cloud & optimized: This is another major boost feature added to MVC6 application. Now it comes integrated to the cloud with Microsoft Azure and also the optimizing and monitoring tool provided by Azure, i.e. Application Insights.
We will have a walk through of adding the cloud Web application and then a brief on Application insights as well.
Boosted Dependency Injection: Now MVC6 application has in built and integrated dependency injection facility. There is no more need for the packages like, Ninject, Unity, Structure Map3 and all. The code for the configuration setting for the dependency injection is added inside the StartUp.cs class file as below:
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to add services to the container.
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
// Add framework services.
services.AddApplicationInsightsTelemetry(Configuration);
services.AddEntityFramework()
.AddSqlServer()
.AddDbContext(options =>
options.UseSqlServer(Configuration["Data:DefaultConnection:ConnectionString"]));
services.AddIdentity<ApplicationUser, IdentityRole>()
.AddEntityFrameworkStores()
.AddDefaultTokenProviders();
services.AddMvc();
// Add application services.
//Dependency Injection as well
services.AddTransient<IEmailSender, AuthMessageSender>();
services.AddTransient<ISmsSender, AuthMessageSender>();
}The we normally inject the services into the constructor of the controllers. Is’nt that great!!
appsettings.json: As we know there is no Web.config file in our application, but we need to have a place where we have the settings required by the application at all stages. This is this place. In MVC6, they have had a upper hand over the JSON than the XML. 
The connection strings, the other app settings file we used to add inside the Web.config will now be contained here, that to in Json format. An example like below:
"Data": {
"DefaultConnection": {
"ConnectionString": "Server=(localdb)\\mssqllocaldb;Database=aspnet5-AzureWebAppDemo-XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX-XXX;Trusted_Connection=True;MultipleActiveResultSets=true"
}
}global.json: This is a separate folder named Solution Items. here is the global.json file, which contains the solutions’s project references and their dependencies as well. Loos like below:
{
"projects": [ "src", "test" ],
"sdk": {
"version": "1.0.0-rc1-update1"
}
}The appsettings is initialized into the project in the Startup.cs file as below:
var builder = new ConfigurationBuilder()
.AddJsonFile("appsettings.json")
.AddJsonFile($"appsettings.{env.EnvironmentName}.json", optional: true);The App_Start which had the RouteConfig.cs file also goes missing. In MVC is present inside the Startup.cs file as below:
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env, ILoggerFactory loggerFactory)
{
app.UseMvc(routes =>
{
routes.MapRoute(
name: "default",
template: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}");
});
}Thus, lets have a look at the entry point of the application:
// Entry point for the application.
public static void Main(string[] args) => WebApplication.Run(args);Another nice feature is the segregation of the Models & View Models. The Model now only will deal with the Db Entities and the context, where as the ViewModel will deal with the model classes which are required in the View binding.
This was just a brief about MVC6, more information and application building will be shown in the upcoming articles on MVC6. Now lets jump start the deployment to azure.
Head start Deployment
Now lets discuss creating a new MVC6 project from VS 2015 and then deploying to Azure, mostly I will pictorially explain you which will help understand better.
- Step 1: Create a brand new project from the Visual Studio 2015 templates. Select the cloud directly and then the Web project as we will be deploying our application to azure.
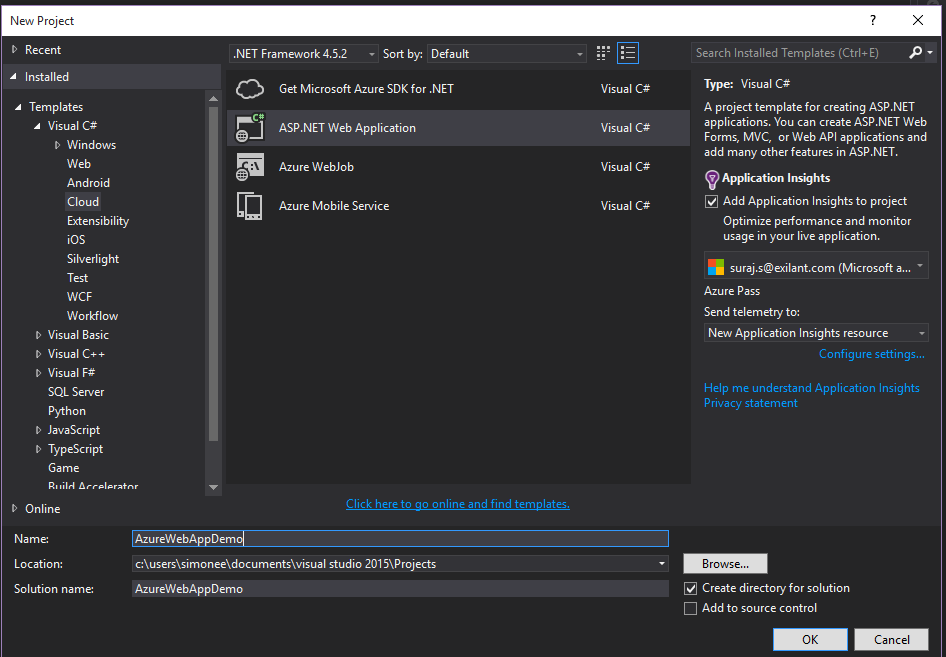
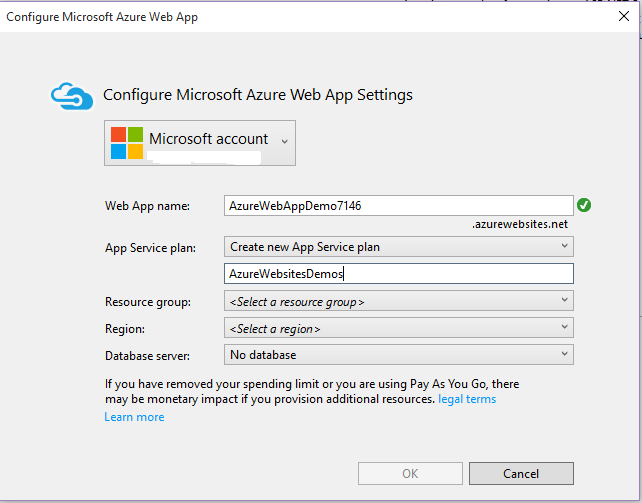
- Step 2: Then after giving name for the project, another window will prompt which will ask for the Microsoft Azure configurations. Web App Name, which will actually be the URL for the application after hosted on cloud.
Then asks for the Application Service under which the application will be registered and deployed.
Region is another important factor which might come handy in the performance of the application. Thus, we select East Asia here.
If asked for the Database server and the application required we add a new database server or use any existing database. We skip for now the database integration.
- Step 3: After setting up, we land in creating our first web application and the structure is like below:
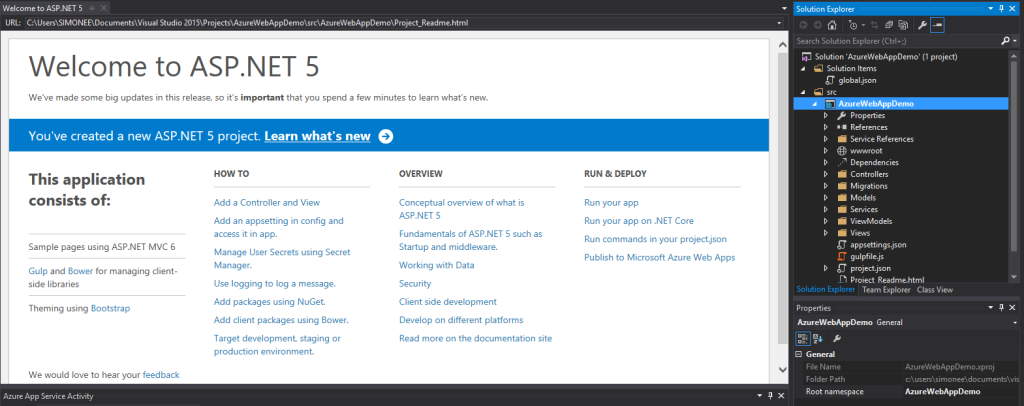
- Step 4: Lets have a look at project structure which gets created.

- Step 5: Lets now publish and deploy our web application. Right click on the project and click ‘Publish’. We then see a window pop up like below:
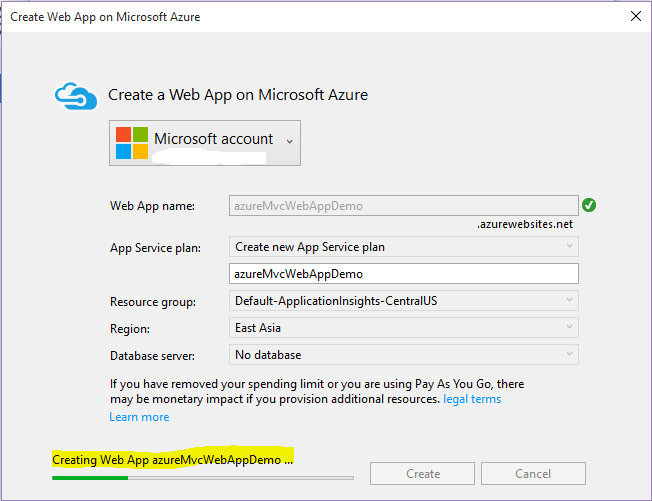
- Step 6: This will now create an Application Service(Webservice) on Azure portal and also deploy our Web Application as a new Website. The status can be seen under Azure Activity :
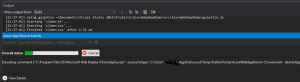
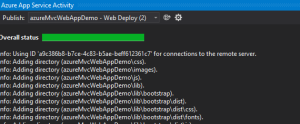
The above images are the over all status and the name of the publish package that got deployed. -
Step 7: Then navigate to the Azure portal, already notifications would be highlighted to let you know that web site is now hosted and you can browse.
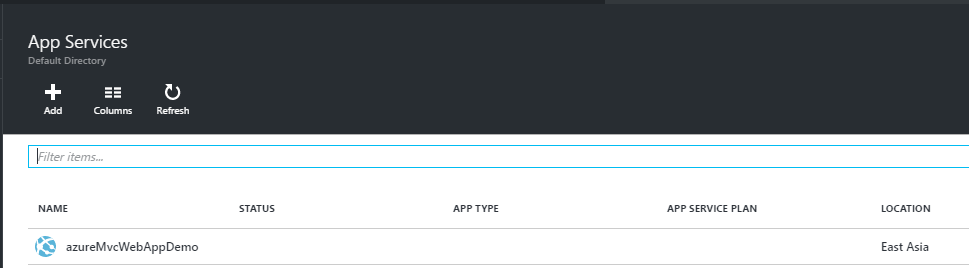
The status app type and the app status will update in a few minutes.
Conclusion
Thus, once the website is hosted on Azure, we can browse and run our application and share with anyone to navigate through our application. We came to know in this article how easy it is to deploy to cloud in the latest builds, making the lives of developers much easier. I will be sharing and covering the Application Insights in the next article which will follow this up. I hope this has helped in learning some facts about MVC6 and please post your feedback. Application Insights– upcoming.