Topics to be covered
- What is HTML5
- Semantic Markup
- Forms
- Audio & Video
- Data Storage
- What is CSS
- Inheritance & Cascading
- Style Sheets
- Page Layout & Nav bars
- Web Matrix & Demo
What is HTML5?
HTML5 is the 5th version of HTML. Now wonder what is HTML!!
HYPER TEXT MARKUP LANGUAGE. Caps means I am shouting, but it is a shout that needs to be done. Lets understand each word of it.
Hyper as we all know means to get exaggareted or tempered on something. Here it also has a similar meaning, when taken together with
Hyper Text. This means it gives a simple text a hyper meaning. For instance, a simple text video written changes to a iframe where a video is played when rendered on a browser.
HTML is used to create web pages in web applications. WebPages!! In a simple way, a page that gets rendered on web is called web page.
Let get some brief on the history also. 🙁 . Though the sadpart but lets get into it a bit.
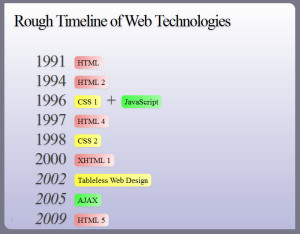
The above image says it all. But I would like to brief something interesting here. HTML4 was to be suppressed by XHTML but W3C(World Wide Web Consortium) never got heavily biased by XHTML.
HTML5 was being secretly developed by WHATG group. HTML5 is a combination of number of technologies and techniques and approaches to web. Thus the HTML5 was so convincing that it was approved by the W3C recently.
Semantic Markup
First lets know what is semantic! Semantic in dictionary means it is related to meaning in language and logic. That means what logic/idea you get you derive text out of it and HTML5 gives you the desired output. Like for instance,
You think of a logic where you want user to show the amount of download/upload done or progressed. So here we derive the word progress, and HTML5 gives the tag element
Doctype html simplified
<!Doctype html> has been simplified prior to the previously used has been replaced. Just for information, the syntax is case-insensitive.
The image shows, the html starts with the doctype that lets the web browser know that the document being loaded is of type “html”.
Then is thethat states that the html doc is written in english language.
Forms in HTML
HTML Forms are required when you want to collect some data from the site visitor. For example during user registration you would like to collect information such as name, email address, credit card, etc. A form takes the input from the user and stores them
in the server.
Different attributes are:-
- Action:- Backend/Server side code for storing the records.
- Method:- GET/POST, suggests whether to post data/input or get the data input into the form elements.
- Target:- Specify the window/frame where the end result script will be shown, _blank,_self,_parent.
We will see the example in the demo codes.
Audio & Video
In HTML5, there is no need anymore to use the iframes and load the videos/audios. The HTML5 audio and video tags make simple to add media files to website. We just need to set src attribute to let the frame know which video or audio to play, and also set the other attribute
like loop which plays the media file continously, autoplay lets the media file play when the page loads, controls let the controls icons to view on the frame and height width.
Data Storage
This is a very new concept that has been introduced in HTML5 that helps store data incase there is slow connection. Thus this introduces a balance between server side and the client side processing. This is an extension to cookies.
There are two types of data storage schemes,
- Session Storage
- Local Storage
Local Storage
Before HTML5 was introduced, data was stored in cookies and code was maintained on the server only. But now in HTML5, local storage is introduced where data can be stored in large bulk, without affecting the performance of the website. Unlike the cookies, the storage limit is 5MB.
The Local storage is based on the domain. All pages can access the stored data those are from the same domain as the data gets stored locally.
window.localStorage: (stores without expiration time)
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 |
function initiate(){ var saveButton = document.getElementById("save"); var retrieveButton = document.getElementById("retrieve"); var deleteBUtton = document.getElementById("delete"); saveButton.addEventListener('click', saveItem); retrieveButton.addEventListener('click', retrieveItem); deleteBUtton.addEventListener('click', deleteItem); } function saveItem(){ var firstName = document.getElementById("fName").value; var lastname = document.getElementById("lName").value; var email = document.getElementById("eMail").value; var address = document.getElementById("add").value; var comments = document.getElementById("comments").value; localStorage[firstName] = address; document.getElementById("fName").value = ""; } function retrieveItem(){ var data = document.getElementById("retrieveData"); var firstName = document.getElementById("fName").value; var add = localStorage[firstName]; data.innerHTML = add; } function deleteItem(){ if (confirm('Delete?')) { var firstName = document.getElementById("fName").value; localStorage.removeItem(firstName); alert("Deleted"); document.getElementById("retrieveData").value = ''; } } addEventListener("load", initiate); |
Session Storage
Before HTML5 was introduced, data was stored in cookies and code was maintained on the server only. But now in HTML5, session storage is introduced where data can be stored, without affecting the performance of the website. Unlike the Local Storage, in the session storage, the data
gets stored in session and also depends on the session. Once the session expires, the data is lost. But this not the case in the local storage the data persists without time limit, where as in the session storage the data is lost once the session expires or the browser is closed.
window.sessionStorage:-(stores with session expire time)
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 |
function initiate(){ var saveButton = document.getElementById("save"); var retrieveButton = document.getElementById("retrieve"); var deleteBUtton = document.getElementById("delete"); saveButton.addEventListener('click', saveItem); retrieveButton.addEventListener('click', retrieveItem); deleteBUtton.addEventListener('click', deleteItem); } function saveItem(){ var firstName = document.getElementById("fName").value; var lastname = document.getElementById("lName").value; var email = document.getElementById("eMail").value; var address = document.getElementById("add").value; var comments = document.getElementById("comments").value; sessionStorage[firstName] = address; document.getElementById("fName").value = ""; } function retrieveItem(){ var data = document.getElementById("retrieveData"); var firstName = document.getElementById("fName").value; var add = sessionStorage[firstName]; data.innerHTML = add; } function deleteItem(){ if (confirm('Delete?')) { var firstName = document.getElementById("fName").value; sessionStorage.removeItem(firstName); alert("Deleted"); document.getElementById("retrieveData").value = ''; } } addEventListener("load", initiate); |
Here we end discussing on the HTML5, now lets move onto the CSS
What is CSS
CSS- Cascading Style Sheet. Lets discuss the definition word by word.
“Cascading” in this context means that because more than one stylesheet rule could apply to a particular piece of HTML, there has to be a known way of determining which specific stylesheet rule applies to which piece of HTML.
Style sheet as it explains itself is a sheet where styles are specified for the HTML elements on the pages. Descendents inherit style from ancestors. More Specific styles win over the inherited style.
Identifiers, Class & Pseudo Elements
Identifiers are represented in an element as id=”IDENTIFIER NAME”. These are the unique peices that can only be attached/added to a specific element. These are accessed through the character “#”.
Classes are represented in an element as class=”CLASS NAME”. These are the peices that are defined once in the Style sheet and can be used in multiple elements. These are accessed through the charachter “.”(dot).
Pseudo elements are :first-child
:last-child
:nth-child(odd/even)
These elements are predefined and are accompanied or they succeed the letters of the html tag elements, like:-
Specificity Rule
A very nice concept to know for using CSS in an effective manner. Lets look into the concept.
Id : a ex:- ul ol li .red
Class: b a = 0; b=1; c=3 => sp = 013
Pseudo Elements: c
As you can see in the above example, we can see ID has the highest specificity. see in the example i.e. ul ol li .red, there is one class so b=1, pseudo elements are 3, so c=3. Thus the specificity turns out to be 013.
Taking another example, ul #listID .redList, here the specificity turns out to be a=1;b=1;c=1 so 111.
Page Layout
- Layout contain boxes, that is block-level elements
- Use HTML Semantic tags
- Else if Semantic tag don’t work, use
- For making a column: set width
set float - For Layout, start with content & Identify boxes.
- Is a set of links
- List of different areas/pages using
- Remove the bullets {list-style:none}
- Eliminate padding & margins
- Set display to inline-block to eliminate new lines
- Style the links (as you wish)
Nav Bars
WebMatrix
This is a very light weight, opensource tool provided by Microsoft that can be downloaded from the link below:-
For Web Matrix
Web Matrix can be downloaded also from the Microsoft Web Platform Installer from the below link:-
For Web Platform Installer
Finally the demo codes will look like below when run on browser:-








