With 20% faster performance than .Net Core 1.X, core 2.0 is in the lime light. Optimizing to the core the .Net core 2.0 is the next big thing for the Microsoft Developers.
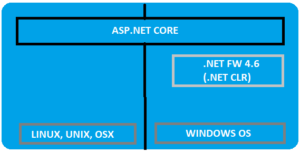
A modular framework uniting the MVC and Web API into a single programming Model running on .Net framework or .Net core run-time but can run on any platform. Highly flexible in deploying to cloud and since cross platform, the demand among the developers increases.
Asp.Net Vs Asp.Net Core
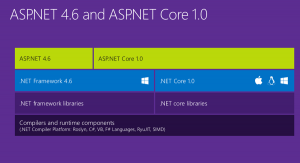
Asp.Net Core is runtime and executes applications built for it. Asp.Net core application is also .Net Framework application because of the .Net core libraries are used for both the core and .Net framework applications. Here the thing to notice is Asp.Net core is built on top of both .Net framework & .Net Core where as the Asp.Net is now being termed as .Net Framework. Check the image below (from Blogs )
Asp.net Core libraries/dependencies are self-contained, most of the packages are downloaded from Nuget but can run on windows, linux & Mac where as in Asp.Net the packages are self contained but can only run on windows.
Based on the .Net Core CLI (Command Line Interface) on which the IDE (Integrated Development Environment) relies on. It is the cross platform tool chain for developing .Net applications irrespective of the platform.
Visual Studio as IDE has support for running on Windows and MacOS. Visual studio code can be used as IDE on windows, MAC and Linux systems as well.
Directly .Net Core CLI can be used on the Command window to execute the .Net applications.
dotnet new console dotnet build --output /build_output dotnet /build_output/my_app.dll
More about .Net Core 2.0
The latest of the Core versions now in the market. With the command line interface it is just few command away from creating a .Net Core 2.0 application. .Net core 2.0 now comes with the Entity framework 2.0. To start with the .Net Core 2.0, one just needs to download and install the .Net core 2.0 SDK
Creating a small and simple application using CLI

.Net Core 2.0 has a lot of performance improvements. One of the best improvements in .Net Core 2.0 is Razor Pages. Razor pages in .Net core 2.0 MVC projects are enabled by default using the services.AddMvc();
Now whats new in the integration of Razor Pages! In the Razor Pages now there is no direct coupling with the hard bound Controller we used to create and adding views to them and then routing through the controllers and Actions.
Now, we can directly create a folder and add a .cshtml page. For example,
We add a cshtml file named- “CoreTest.cshtml”
@page <h1>Hello Core 2.0!</h1>
Here the routing would be “/CoreTest”. Simple and Crisp! Interesting thing is the precious page route was /CoreTest, now it can be customized and rerouted to the customized route to suppose “/core-test”.
services.AddMvc()
.AddRazorPagesOptions((opts) =>
{
opts.Conventions.AddPageRoute("/CoreTest", "core-test");
});Razor compilation is easier and is automatically compiled during the publishing of the package or the application.
MvcRazorCompileOnPublish is the property that is set to true by default. We can set it to false to avoid this auto compilation.
<PropertyGroup> <TargetFramework>netcoreapp2.0</TargetFramework> <MvcRazorCompileOnPublish>false</MvcRazorCompileOnPublish> </PropertyGroup>
The .Net core 2.0 simplified the Program.cs class file as compared to the .Net Core 1.x.
For .Net Core 1.X
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
var host = new WebHostBuilder()
.UseKestrel()
.UseContentRoot(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory())
.UseIISIntegration()
.UseStartup()
.UseApplicationInsights()
.Build();
host.Run();
}
}For .Net Core 2.0
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
BuildWebHost(args).Run();
}
public static IWebHost BuildWebHost(string[] args) =>
WebHost.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.UseStartup()
.Build();
}Now migrating a .Net Core 1.X project/application to .Net Core 2.0 is easy as well. We will cover the Migration Steps in the upcoming articles without letting down the scope of this article.
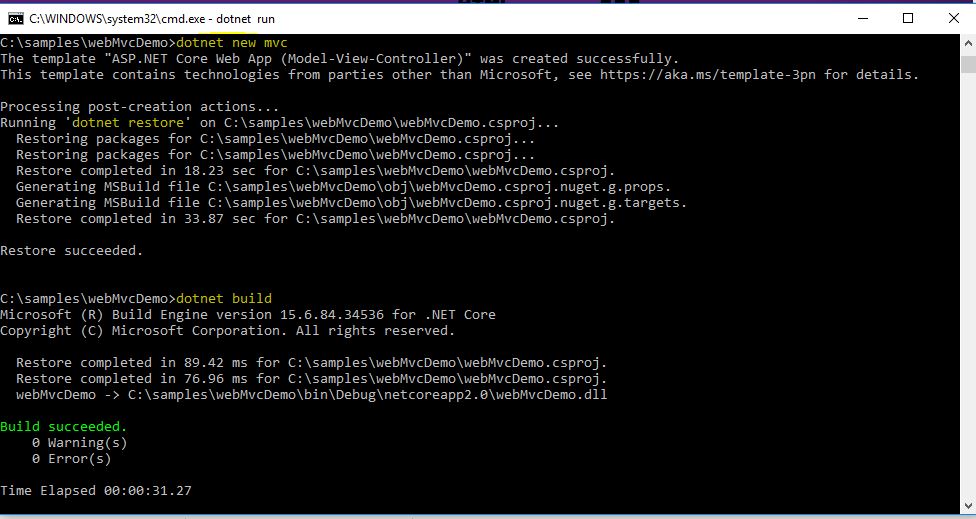
Lets create a MVC Web Application from Command Line
Using the command line interface we can create different types of dotnet applications without using the GUI. The commands to be used are:
- dotnet new -type:- There are different types of dotnet application that can be created using the command new and specifying the type. Like earlier we created a console application, so the command was “dotnet new console”. Similarly for a normal web project, the command would be “dotnet new web”. For MVC application, the command is “dotnet new mvc”.
- dotnet restore:- Restores the packages and assemblies while compiling the project. This is auto run during the new project creation process as well.
- dotnet build:- This is the build command which runs before running the application required to compile the application.
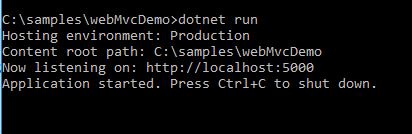
- dotnet run:- This command actually runs the appliction, hosting using the IIS and localhost port.
The entire commands on CMD looks like below:
The project after creation looks like:

The run command on CMD looks like:
There are many more interesting features introduced in .Net Core 2.0. We will be covering the features in detail in the upcoming articles.
]]>- Welcome to C#
- Working with Variables, Operators & Expressions
- Understanding your first C# program
Welcome to C#
C# .NET is a powerful language, which is generally called Component Oriented Language. Now we have heard of Object Oriented Language, but what is component oriented language!! Though the difference is fairly blurr and thin, but the reason why this new concept came associated with C# is that a new technique was to be introduced that would develop software combining some pre-existing features (OOP) and welcoming some new components. Some of the components are :
- Properties
- Methods
- Events
- Attribute(Metadata-Data about Data)
- Assemblies/Packages
Another major characteristic is introduction to SOC and SOA. SOC is separation of concern via partial classes in c# and SOA is service oriented architecture concept while programming in C#.
Versions in C#
I am mentioning below the versions till date. Data issued from C# Indepth. Please visit or follow the book to know more about the different Versions.
- C#- version 1
- C#- version 2: As mentioned, in this version, Generics, Nullable types(), anonynous types & Iterators(blocks) were introduced.
- C#- version 3: As mentioned implicit typing, object and collection initializers, anonymous types, automatic properties, lambda expressions, extension methods, query expressions were introduced.
- C#- version 4: As mentioned dynamic typing, optional parameters, named arguments, and generic variance were introduced.
- C#- version 5: As mentioned asynchronous functions, caller info attributes(This is a very new concept and an interesting one too. These attributes track information about the calling methods/properties and many more.), and a tweak to foreach(one of the example is Parallel.Foreach(with Lambda expression)) iteration variable capture were introduced.
A small incident to share, I always wondered why C sharp?? It is kind of a successor for C++ or what? I always wondered, and I feel many beginner developers would be wondering. Thanks to Wiki the datawarehouse for every bit of concept in the world for letting me know why? Without any delay, straight from the WIKI,
The name “C sharp” was inspired by musical notation where a sharp indicates that the written note should be made a semitone higher in pitch. The sharp symbol also resembles a ligature of four “+” symbols, which thus implies that it is an increment of C++.
Now lets get along and start learning from basics.
Camel & Pascal Case Notations
Every time a developer gets into these concepts, but sometimes beginners like me would wonder what these actually are!!.
Camel case are used for naming fields where as Pascal case are used for naming properties, function names. In Pascal case, the starting letters in the multiword name are capitalized where as in Came case except the very frst letter all are capitalized like below:
- Pascal Case:- GetSumFromNumbers
- Camel Case:- getFirstNumber
Working with Variables, Operators & Expressions
Before getting into the variables, lets get into what is an identifier. Identifiers are the names that are used to identify elements in the program. In C#, there are certain conventions to be followed:
- Only letters are allowed(may it be uppercase or lowercase), digits and underscore(_) characters are allowed.
- An identifier should always start with a letter.
For example, _getSum, GetSum, Get_sum are valid identifiers. Just to remember or keep in mind everytime that C# is case sensitive so getSum and GetSum are different and give different meanings.
Keywords, there are many keywords that are predefined in C#, for more info on the keywords, follow the below link: C# keywords
Now lets get back to our topic of discussion, variables. A variable is a location with memory or storage location that stores/holds a value. A variable in a program holds a unique name, its like madatory to give it a unique name. A variable holds temporary information. A variable is used to get the value that it holds after assigning. Below I specify the naming conventions to be followed while declaring variables specified by Microsoft .NET team:
- Underscores are advised not to be used
- Case differing names for variables should be avoided. Like, abcTest or AbcTest to be used in the same file and same time. This would also mean Identifiers with same name and different case should be avoided.
- It is advised to start the name with a lowercase. This would be consistent through out as it would lead to easy mantenance.
- Camel case notations should be used, forexample, abcTest, myVariable, as such.
Declaring Variables is easy and simple. Usually keyword var is used when the type is to be implicitly decided. If any datatype is already used during declaring the vriable, then it is explicitly typed.
var setAge; //implicitly typed int setAge; //explicitly typed setAge = 45; //values assigned
As in the above peice of snippet, you can see the statement ends with a semicolon “;” that as simple marks the end or compiler to know that the statement ends here. Equals operator is used to assign the value to the declared variable. C# also uses same the operators that we as developers have been using in the former programming languages (+(plus), -(subtraction), *(asterix/multiplication), /(divide) and also the modulo operator(%)). These are as we know called the arithmetic operators. We cannot apply the arithmetic operations on the datatypes except int(integer type) in a similar way.
int a = 4 + 3; string b = "4"+"3"; Console.Writeline(a);//Prints 7 Console.Writeline(b);//Prints 43 not 7
However using explicit conversion, string can be converted into integers. For incrementing the values, the increment and decrement operators are also strongly followed in C#.
count= count + 1; //Can be incremented but should not be written like this count++; //This is how increment should be done count = count - 1; count = count--;
Understand your first C# program
As we all know, every program follow a common rule that is Input, Process & Output. Lets have go at it.
using System;
namespace ConsoleDemoApplication
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string firstName; //Variable for storing string value
string lastName;
//Displaying message for entering value
Console.WriteLine("Please Enter Your First Name");
//Accepting and holding values in name variable
firstName = Console.ReadLine();
Console.WriteLine("Please Enter Your Last Name");
lastName = Console.ReadLine();
//Displaying Output
//{0}{1} take the variable names that are assigned during the runtime by the user
Console.WriteLine("Welcome {0} {1} in your first C-sharp program", firstName,lastName);
//Holding console screen
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}When we run the above program, we get the below output. I am showing the output step wise, so that you get to know the importance of the Console.WriteLine & Console.ReadLine
. As we see in the image, the console window opens up when the project runs and asks for the first name as we see in the program first comes Console.WriteLine(), then when user enters the name Console.ReadLine(), plays its role and stores it in the variable memory firstName.
As we see in the image, the console window opens up when the project runs and asks for the last name as we see in the program first comes Console.WriteLine(), then when user enters the name Console.ReadLine(), plays its role and stores it in the variable memory lastName.
Now when a final enter is pressed by the user with curosity to know what the program gives! Yes it gives the desired out put. It concats the variables where the names/values entered by the user are temporarily stored in memory. {0} {1}, this actually contain the values entered by the user when asked and as mentioned concats the input and displays the full name as the output. This could also have been achieved by using the “+” operator like:
string fullName = firstName + " " + lastName; //+ operator concats the strings
Console.WriteLine("Welcome {0} in your first C-sharp program", fullName);There are many libraries that may be used in your program. These libraries need to be mentioned at the top of your program i.e. which is called Namespaces and they are used using a using keyword.  Yes so many use…!!
Yes so many use…!!
When on the console window, something needs to be displayed, Console.WriteLine() is used and when we need to take the Input from the user and store in memory, Console.ReadLine() is used. This is a simple and basic difference. The {0} used in our program, acts as asimple placeholder where the dynamic values are used by specifying the argument at the end. The many the arguments, the many the placeholders to be used.
Conclusion
Thanks guys for having patience and reading through. This is what I could cover in the first part and will continue some more interesting topics in the second part. Lets learn Lets explore and Lets share…
Any suggestions and corrctions are humbly accepted as we all keep learning at every step.
Follow the C# 6 New Features for more info on the upcoming version C# 6.
Refrences
- Visual C# .NET- John Sharp and Jon Jagger
- MSDN
- Csharp Tutorials